자료구조
Tree(1) - Tree 구현
blackbearwow
2022. 7. 10. 13:09
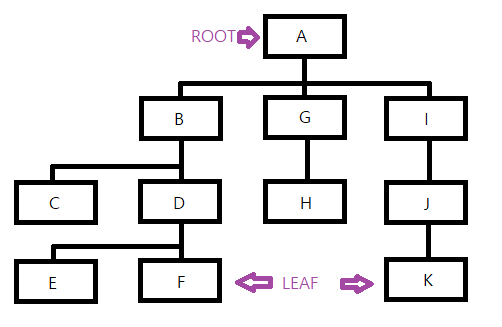
노드의 깊이(Depth) : 루트 노드에서 해당 노드까지의 경로의 길이
레벨(Level) : 깊이가 같은 노드의 집합
트리의 높이(Height) : '가장 깊은 곳'에 있는 잎 노드까지의 깊이
노드의 차수(Degree) : 그 노드의 자식 노드 개수
트리의 차수(Degree) : 트리 내에 있는 노드들 가운데 자식 노드가 가장 많은 노드의 차수
| 노드 | 노드의 깊이(Depth) | 노드의 차수(Degree) |
| A | 0 | 3 |
| B | 1 | 2 |
| C | 2 | 0 |
| D | 2 | 1 |
| E | 3 | 0 |
| F | 3 | 0 |
| G | 1 | 1 |
| H | 2 | 0 |
| I | 1 | 1 |
| J | 2 | 1 |
| K | 3 | 0 |
레벨 0 : {A}
레벨 1 : {B, G, I}
레벨 2 : {C, D, H, J}
레벨 3 : {E, F, K}
트리의 높이 : 3
트리의 차수 : 3
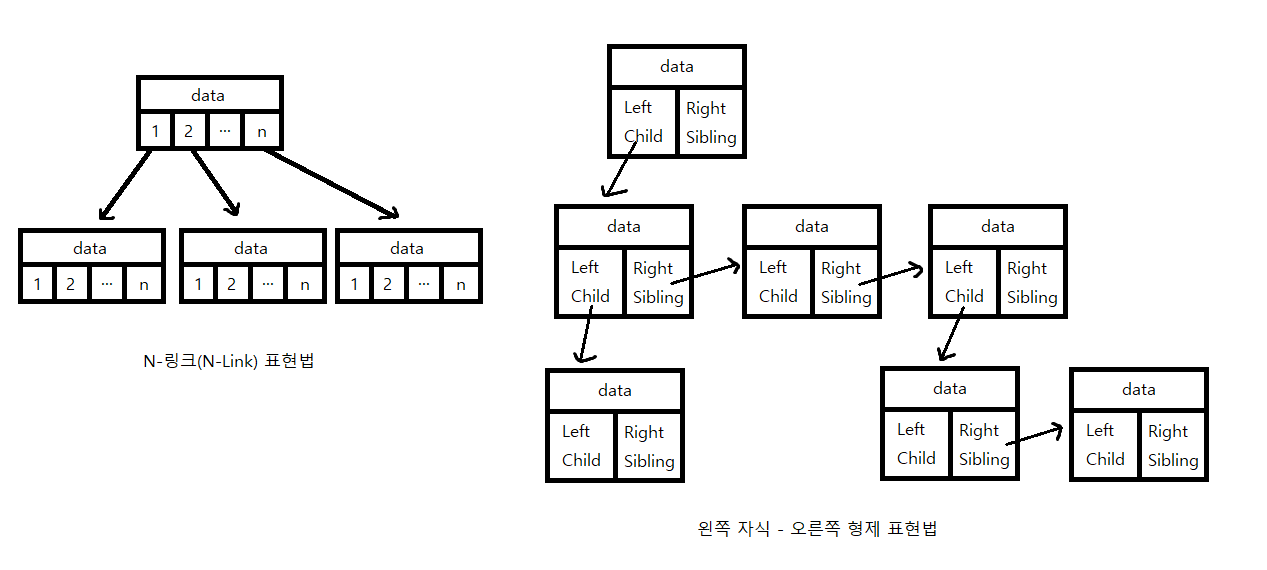
노드 표현법은 N-Link 표현법과 왼쪽 자식-오른쪽 형제 표현법이 있다. 교제에서는 후자의 방법으로 구현한다.
// gcc -o Test_LCRSTree.exe Test_LCRSTree.c LCRSTree.c; ./Test_LCRSTree.exe
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef char ElementType;
typedef struct tagLCRSNode
{
struct tagLCRSNode* LeftChild;
struct tagLCRSNode* RightSibling;
ElementType Data;
} LCRSNode;
LCRSNode *LCRS_CreateNode(ElementType NewData)
{
LCRSNode *NewNode = (LCRSNode *)malloc(sizeof(LCRSNode));
NewNode->LeftChild = NULL;
NewNode->RightSibling = NULL;
NewNode->Data = NewData;
return NewNode;
}
void LCRS_DestroyNode(LCRSNode *Node)
{
free(Node);
}
void LCRS_DestroyTree(LCRSNode *Root)
{
if (Root->RightSibling != NULL)
LCRS_DestroyTree(Root->RightSibling);
if (Root->LeftChild != NULL)
LCRS_DestroyTree(Root->LeftChild);
Root->LeftChild = NULL;
Root->RightSibling = NULL;
LCRS_DestroyNode(Root);
}
void LCRS_AddChildNode(LCRSNode *Parent, LCRSNode *Child)
{
if (Parent->LeftChild == NULL)
{
Parent->LeftChild = Child;
}
else
{
LCRSNode *TempNode = Parent->LeftChild;
while (TempNode->RightSibling != NULL)
TempNode = TempNode->RightSibling;
TempNode->RightSibling = Child;
}
}
void LCRS_PrintTree(LCRSNode *Node, int Depth)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < Depth; i++)
printf(" ");
printf("%c\n", Node->Data);
if (Node->LeftChild != NULL)
LCRS_PrintTree(Node->LeftChild, Depth + 1);
if (Node->RightSibling != NULL)
LCRS_PrintTree(Node->RightSibling, Depth);
}
void LCRS_PrintNodesAtLevel(LCRSNode *Root, int Level)
{
LCRS_PrintTreeAtLevel(Root, 0, Level);
printf("\n");
}
void LCRS_PrintTreeAtLevel(LCRSNode *Node, int Depth, int Level)
{
if(Depth == Level)
printf("%c ", Node->Data);
if (Node->LeftChild != NULL)
LCRS_PrintTreeAtLevel(Node->LeftChild, Depth + 1, Level);
if (Node->RightSibling != NULL)
LCRS_PrintTreeAtLevel(Node->RightSibling, Depth, Level);
}
int main( void )
{
/* 노드 생성 */
LCRSNode* Root = LCRS_CreateNode('A');
LCRSNode* B = LCRS_CreateNode('B');
LCRSNode* C = LCRS_CreateNode('C');
LCRSNode* D = LCRS_CreateNode('D');
LCRSNode* E = LCRS_CreateNode('E');
LCRSNode* F = LCRS_CreateNode('F');
LCRSNode* G = LCRS_CreateNode('G');
LCRSNode* H = LCRS_CreateNode('H');
LCRSNode* I = LCRS_CreateNode('I');
LCRSNode* J = LCRS_CreateNode('J');
LCRSNode* K = LCRS_CreateNode('K');
/* 트리에 노드 추가 */
LCRS_AddChildNode( Root, B );
LCRS_AddChildNode( B, C );
LCRS_AddChildNode( B, D );
LCRS_AddChildNode( D, E );
LCRS_AddChildNode( D, F );
LCRS_AddChildNode( Root, G );
LCRS_AddChildNode( G, H );
LCRS_AddChildNode( Root, I );
LCRS_AddChildNode( I, J );
LCRS_AddChildNode( J, K );
/* 트리 출력 */
LCRS_PrintTree( Root, 0 );
LCRS_PrintNodesAtLevel(Root, 0);
LCRS_PrintNodesAtLevel(Root, 1);
LCRS_PrintNodesAtLevel(Root, 2);
LCRS_PrintNodesAtLevel(Root, 3);
/* 트리 소멸시키기 */
LCRS_DestroyTree( Root );
return 0;
}